IVF or in vitro fertilization is the practice of adding sperm cells to a female's eggs in laboratory settings. It is called in vitro, which means glass, because it can only be done in glass containers.
Getting Started
IVF procedures are undertaken by couples due to infertility problems in either the male or female or both. Before IVF procedures can take place, screening is done for both the male and the female. Females are subjected to different diagnostics to check the ovary, menstrual cycle and response to follicle-stimulating drugs. These tests can also be used to estimate the number of eggs per cycle and the appropriate amount of gonadotropin hormone to be used.
A waiver is signed by both parties, the requesting couple and the clinic, to protect both from legal responsibilities. Signing the waiver means consenting to the treatment applied by the clinic, understanding the risks and complications and volunteering themselves to the IVF procedures.
IVF Process
- IVF procedures begin by giving stimulation drugs. Usually human gonadotropin hormone is used to increase follicle stimulation and thus produce more eggs during the next monthly cycle. Tests are done 2-3 days after the drugs were induced to check the development of the eggs. To achieve the proper egg count needed, at least 3 follicles should each produce an egg. For females below 40 years of age, about 90% can attain this minimum standard.
- Ultrasound is done, generally after 36 hours, to confirm that the eggs have already been released. The next step would be to take out the eggs from the vagina using a transvaginal procedure or laparoscopy. Laparoscopy is less frequently used due to more risks. This procedure can be quite painful that is why anesthesia is given. Egg retrieval will only last for 5 to 15 minutes. Post-operative cramping can be common after the procedure, while rare complications include intra-abdominal bleeding or infection. Recovery only takes 1-2 hours and the woman can be discharged after.
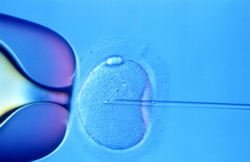
- Once the egg aspiration is done, the eggs are immediately sent to the lab and put in a special fluid. Sperm from the partner is placed in the same container or is injected directly to the egg. Both are left and incubated in a growth medium which is rich in nutrients specifically for fertilization.
- The fertilized embryos are monitored for 2-5 days before they are transferred to the uterus to develop. Most clinics will wait until the 7th day or the blastocyst stage to ensure that the embryos chosen for transfer are fit to develop. Furthermore, this helps reduce the risk of having multiple pregnancies.
Embryologists will pick out the best embryos to be transferred which are determined by the number of cells and consistency of growth shown by each. These are then transferred via a catheter passed through the vagina and cervix. There is no pain or discomfort felt by the woman during this last step in the IVF procedures. After which, the couple will have to wait if the pregnancy will progress.
If the couple was able to produce a number of eggs and sperm cells with excellent quality, they are recommended to have cryptopreservation. If ever the current IVF procedures fail, they can make use of the preserved eggs and sperm for the next cycle.
