Infertility is a condition that impairs the ability to conceive a baby. Almost 10% of the American population of reproductive age is affected by infertility. There are various options of medical treatments available in the market but when the other less expensive medical treatments fail, they all turn to in vitro fertilization.
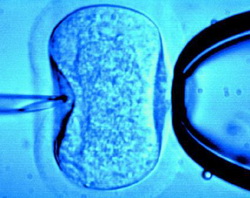
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is an advanced technique used to assist couples with infertility problems to achieve pregnancy. It is a procedure in which the egg is fertilized by a sperm outside the woman's body.
Five basic steps in IVF
1. Stimulation
Before women go through the IVF treatment, they are given fertility drugs to stimulate egg maturation. At this stage, regular transvaginal ultrasound is essential to examine the woman's ovaries to check the hormonal level.
2. Egg retrieval
There are various ways to retrieve eggs from a woman's ovary.
- Transvaginal Oocyte Retrieval is a technique in which a thin needle is inserted in the vaginal opening towards the ovaries. This is used to suck out all eggs and fluids from one ovary at a time. This technique is mostly used during IVF treatment for it is the less invasive and much easier way to retrieve eggs.
- On some rare cases, Pelvic Laparoscopic surgery is done to retrieve the eggs. This method involves cutting a small portion of skin below the abdomen while inserting an instrument called laparoscope.
3. Insemination and Fertilization
After a successful operation of egg retrieval, the eggs are placed in a laboratory dish. Then the eggs and sperm cells are placed in an incubator to promote fertilization called the insemination. In some cases when the chance of fertilization is very low, the sperm is manually injected directly into the egg and this process is called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). Some clinics consider using ICSI automatically to increase the chance of fertilization.
4. Embryo Culture
After the successful insemination and fertilization of the egg, the egg now becomes an embryo. A regular check and monitoring of the growing embryo is done in the laboratory until ready to be transferred back to the woman's uterus.
For some parents who have higher risks of passing genetic disorder, they may consider taking pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD). After 3-4 days of fertilization, this procedure involves manual removing a single cell that display a high tendency of inheriting genetic disorder. Not all centers offer this type of technique.
5. Embryo Transfer
This is the final stage of an IVF procedure. Embryo transfer has two types, namely:
- Day 3 Embryo Transfer: The eggs will be transferred 3 days after a successful fertilization.
- Blastocyst Transfer: Transferring of embryo will happen after 5 days since fertilization or until the blastocyst stage is reached. Some clinics prefer doing blastocyst transfer because at this stage, it is easier to identify a healthy embryo.
Selected embryos will be stored and kept in a catheter. The embryo will be placed inside a rubberized catheter and inserted into the woman's vagina up into her uterus. The embryos will be planted into the uterine lining, hoping for a successful implantation.
Approximately two weeks after, a pregnancy test can be done to identify if the whole procedure of in vitro fertilization (IVF) had been a success.
